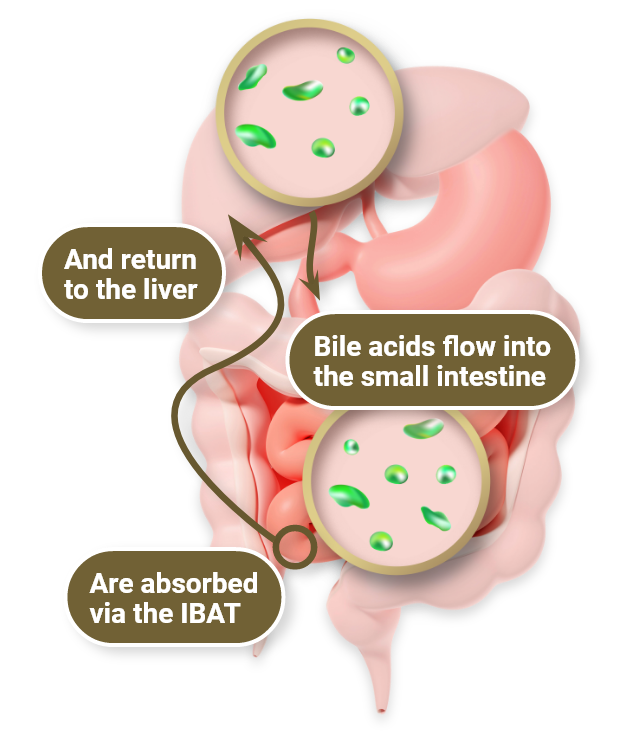
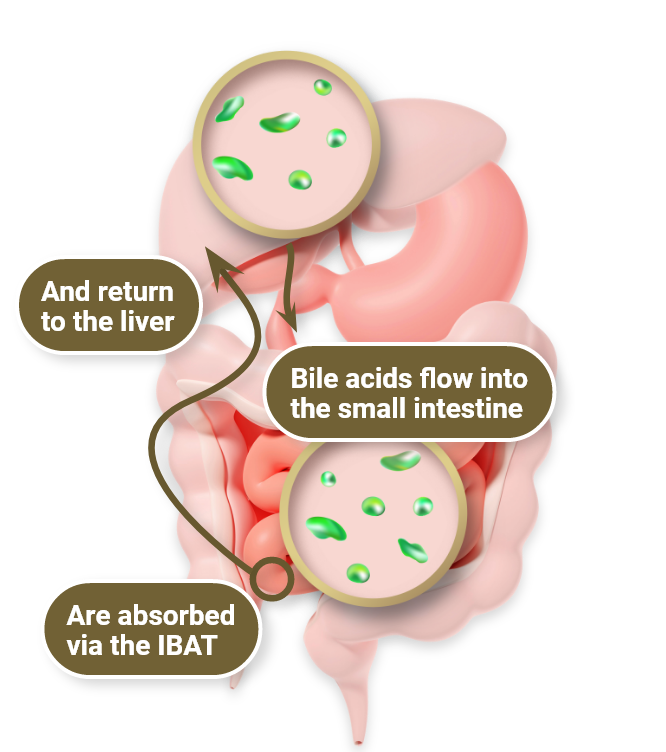
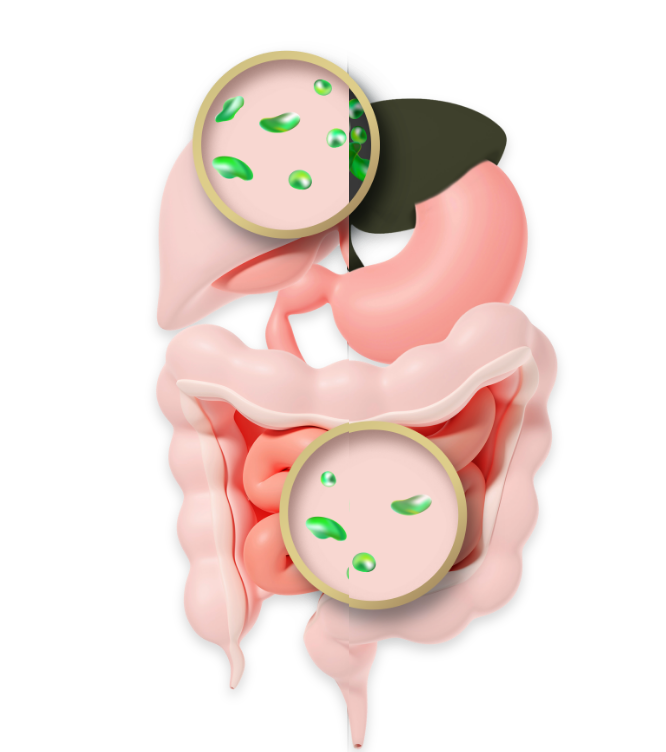
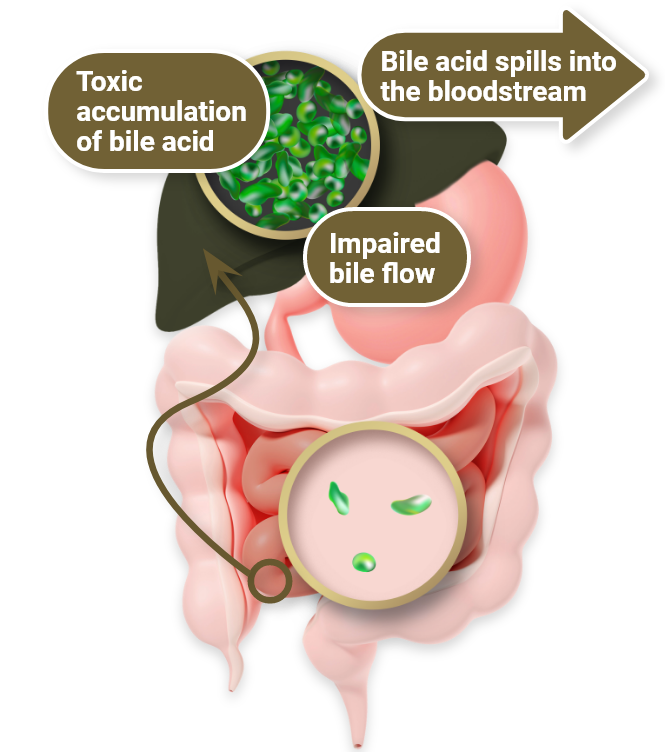
Rare, life-threatening, multisystem disease1
Most common form of inherited disease that causes cholestatic disorder in children2
Up to 70% of cases are caused by de novo mutations and are not inherited from a parent3
1 in every 30,000 to 45,000 individuals are estimated to have an ALGS diagnosis4
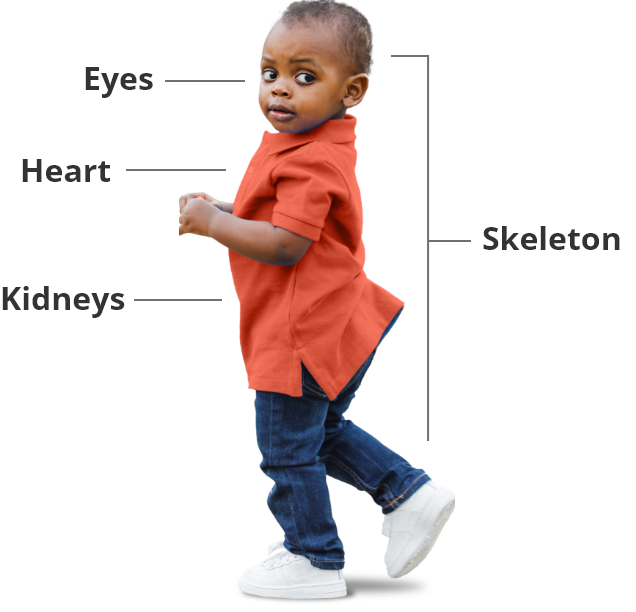

ALGS affects more than just the liver1
As a multiple organ syndrome, ALGS is a progressive disease that affects the eyes, heart, kidneys, and skeleton.
ALGS affects more than just the liver1
As a multiple organ syndrome, ALGS is a progressive disease that affects

Pruritus is a debilitating and challenging symptom of ALGS that can lead to many consequences, including5
Cutaneous mutilation, scarring5
Sleep deprivation5
Disrupted school activity7
Emotional distress5
Impact on caregiver’s personal and family activities8
Impact on caregiver’s employment and finances8
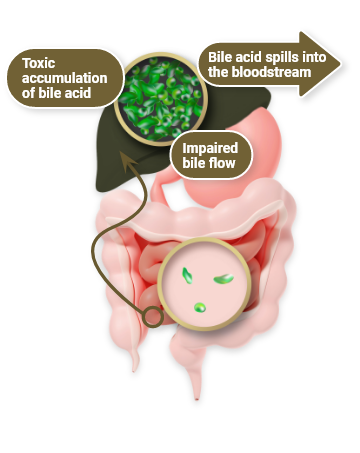
The debilitating nature of cholestatic pruritus may necessitate transplantation1
Pruritus is a debilitating and challenging symptom of ALGS that can lead to many consequences, including:
Cutaneous mutilation, scarring
Cutaneous mutilation, scarring
Cutaneous mutilation, scarring
Cutaneous mutilation, scarring
Risks of surgical intervention1,5
While patients with cholestatic liver disease like ALGS can progress to needing lifesaving surgical intervention like SBD or liver transplant, these options carry significant morbidity and mortality
- Invasive approach
- Potential risk for graft rejection
- Need for lifelong immunosuppression

Explore Bylvay, a non-surgical treatment for cholestatic pruritus in patients with ALGS
ALGS=Alagille syndrome; BSEP=bile salt export pump; IBAT=ileal bile acid transporter; sBA=serum bile acid; SBD=surgical biliary diversion.
References:
- Kamath BM, Baker A, Houwen R, Todorova L, Kerkar N. Systematic review: the epidemiology, natural history, and burden of Alagille syndrome. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018;67(2):148-156.
- Kamath BM, Ye W, Goodrich NP, et al. Outcomes of childhood cholestasis in Alagille syndrome: results of a multicenter observational study. Hepatol Commun. 2020;4(3):387-398.
- Spinner NB, Gilbert MA, Loomes KM, et al. Alagille Syndrome. 2000 May 19 [Updated 2019 Dec 12]. In: Adam MP, Everman DB, Mirzaa GM, et al., editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2022.
- National Organization for Rare Disorders. Alagille syndrome. Updated May 13, 2020. Accessed February 22, 2023. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/alagille-syndrome/?
filter=ovrds-resources - Kamath BM, Stein P, Houwen RHJ, Verkade HJ. Potential of ileal bile acid transporter inhibition as a therapeutic target in Alagille syndrome and progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Liver Int. 2020;40(8):1812-1822.
- Pollock G, Minuk GY. Diagnostic considerations for cholestatic liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;32:1303-1309.
- Srivastava A. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2014;4(1):25-36.
- Mighiu C, O’Hara S, Ferri Grazzi E, et al. Impact of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis on caregivers: caregiver-reported outcomes from the multinational PICTURE study. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022;17(1):1-9.
- Kamath BM, Baker A, Houwen R, Todorova L, Kerkar N. Systematic review: the epidemiology, natural history, and burden of Alagille syndrome. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018;67(2):148-156.
- Kamath BM, Ye W, Goodrich NP, et al. Outcomes of childhood cholestasis in Alagille syndrome: results of a multicenter observational study. Hepatol Commun. 2020;4(3):387-398.
- Spinner NB, Gilbert MA, Loomes KM, et al. Alagille Syndrome. 2000 May 19 [Updated 2019 Dec 12]. In: Adam MP, Everman DB, Mirzaa GM, et al., editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2022.
- National Organization for Rare Disorders. Alagille syndrome. Updated May 13, 2020. Accessed February 22, 2023. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/
alagille-syndrome/? filter=ovrds-resources - Kamath BM, Stein P, Houwen RHJ, Verkade HJ. Potential of ileal bile acid transporter inhibition as a therapeutic target in Alagille syndrome and progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Liver Int. 2020;40(8):1812-1822.
- Pollock G, Minuk GY. Diagnostic considerations for cholestatic liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;32:1303-1309.
- Srivastava A. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2014;4(1):25-36.
- Mighiu C, O’Hara S, Ferri Grazzi E, et al. Impact of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis on caregivers: caregiver-reported outcomes from the multinational PICTURE study. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022;17(1):1-9.